- Published on
Custom Two-factor with Qrcode in django
- Authors

- Name
- Lif
Notes about Google authentication installation
Getting started
In django, I use django-two-factor-auth to setup my google(or other authenticator) qr code and use django-otp to verify my code.
pip install django-two-factor-auth
pip install django-otp
Request by Frontend
Using Vue/React to post request to django-two-factor-auth.
Actually, I only need the put the qr code on my front end and scan it, then use the original api to accomplish the flow.
Look at the source of django-two-factor-auth .
// setup.html
<p><img src="{{ QR_URL }}" alt="QR Code" class="bg-white"/></p>
<p>{% blocktrans trimmed %}Alternatively you can use the following secret to
setup TOTP in your authenticator or password manager manually.{% endblocktrans %}</p>
<p>{% translate "TOTP Secret:" %} <a href="{{ otpauth_url }}">{{ secret_key }}</a></p>
<p>{% blocktrans %}Then, enter the token generated by the app.{% endblocktrans %}</p>
QR_URL is given by backend. Search QR_URL in .py files.
Then got this:
def get_context_data(self, form, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(form, **kwargs)
if self.steps.current == 'generator':
key = self.get_key('generator')
rawkey = unhexlify(key.encode('ascii'))
b32key = b32encode(rawkey).decode('utf-8')
issuer = get_current_site(self.request).name
username = self.request.user.get_username()
otpauth_url = get_otpauth_url(username, b32key, issuer)
self.request.session[self.session_key_name] = b32key
context.update({
# used in default template
'otpauth_url': otpauth_url,
'QR_URL': reverse(self.qrcode_url),
'secret_key': b32key,
# available for custom templates
'issuer': issuer,
'totp_digits': totp_digits(),
})
elif self.steps.current == 'validation':
context['device'] = self.get_device()
context['cancel_url'] = resolve_url(settings.LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL)
return context
The process of generating qr_code is key->rawkey->b32key->otpauth_url->reverse().
I find the generation of key is here:
def get_key(self, step):
self.storage.extra_data.setdefault('keys', {})
if step in self.storage.extra_data['keys']:
return self.storage.extra_data['keys'].get(step)
key = random_hex(20)
self.storage.extra_data['keys'][step] = key
return key
Now, let's focus on the source code:
# In django.views.generic.base.py I found the usage of get_context_data
# It returns all data to frontend via the TemplateResponse format
class TemplateView(TemplateResponseMixin, ContextMixin, View):
"""
Render a template. Pass keyword arguments from the URLconf to the context.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
context = self.get_context_data(**kwargs)
return self.render_to_response(context)
class TemplateResponseMixin:
"""A mixin that can be used to render a template."""
template_name = None
template_engine = None
response_class = TemplateResponse
content_type = None
def render_to_response(self, context, **response_kwargs):
"""
Return a response, using the `response_class` for this view, with a
template rendered with the given context.
Pass response_kwargs to the constructor of the response class.
"""
response_kwargs.setdefault("content_type", self.content_type)
return self.response_class(
request=self.request,
template=self.get_template_names(),
context=context,
using=self.template_engine,
**response_kwargs,
)
The process from QR code generation to saving is just like this: 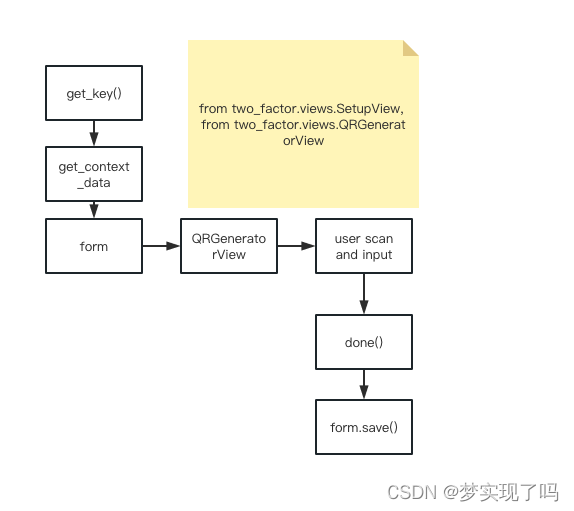
Write my code
After realize all process of this. Now I can write code to cover this process without source code using my own view.
from base64 import b32encode
from binascii import unhexlify
import qrcode
from django.utils.module_loading import import_string
from django.contrib.sites.shortcuts import get_current_site
from two_factor.utils import get_otpauth_url, totp_digits
class QRSetup(View):
default_qr_factory = "qrcode.image.svg.SvgPathImage"
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
key = random_hex(20)
print(f"key is: {key}")
rawkey = unhexlify(key.encode("ascii"))
b32key = b32encode(rawkey).decode("utf-8")
# Get data for qrcode
image_factory_string = getattr(
settings, "TWO_FACTOR_QR_FACTORY", self.default_qr_factory
)
image_factory = import_string(image_factory_string)
content_type = "image/svg+xml; charset=utf-8"
try:
username = get_user_name()
except Exception as e:
username = "lif"
issuer = get_current_site(self.request).name
otpauth_url = get_otpauth_url(
accountname=username, issuer=issuer, secret=b32key, digits=totp_digits()
)
# Make QR code
img = qrcode.make(otpauth_url, image_factory=image_factory)
resp = HttpResponse(content_type=content_type)
img.save(resp)
return resp
class QRCreateListView(generics.ListCreateAPIView):
queryset = TOTPDevice.objects.all()
serializer_class = QrCodeSerializer
permission_classes = (permissions.AllowAny,)
def post(self, request):
key = 0
tolerance = 1
t0 = 0
step = 30
drift = 0
digits = totp_digits()
user = None
try:
request_body = request.data
except Exception as e:
print(e)
key = request_body.get("key")
user = User.objects.filter(username=request_body.get("user"))[0]
try:
TOTPDevice.objects.create(user=user, key=key,
tolerance=tolerance, t0=t0,
step=step, drift=drift,
digits=digits,
name='default')
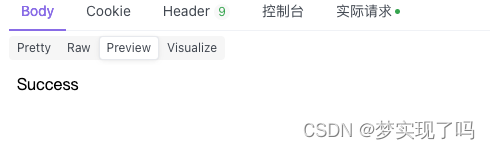
return HttpResponse("Success")
except Exception as e:
print(f"{e}")
return HttpResponse("fail")
Then add url to urls.py
path(
"api/v2/test/", QRSetup.as_view(), name="testOtp"
),
path(
"api/v2/save/", QRCreateListView.as_view(), name="testOstp"
)
Now, we can use Apifox to make request.
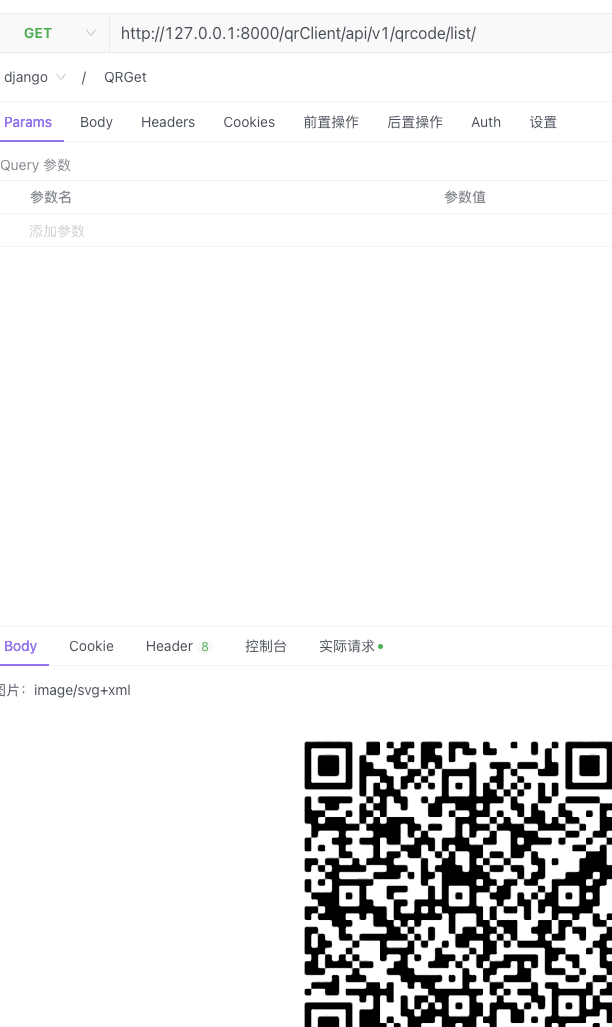
Notice to use the key generated by key = random_hex(20).  And I got success:
And I got success: